Artificial intelligence (AI) is a powerful technology that can benefit society and pose significant risks to human rights, safety, and democracy. To address these challenges, the European Commission proposed a regulation on AI known as the Artificial Intelligence Act (AI Act). The AI Act aims to create a legal framework for trustworthy AI that respects the EU values and principles.
The AI Act introduces a risk-based approach to regulating AI systems based on their potential impact on human rights and society. The AI Act identifies categories ranging from unacceptable to limited risk. Unacceptable risk AI systems violate fundamental rights or threaten safety and security, such as social scoring or mass surveillance. These systems would be banned in the EU. High-risk AI systems are those that have a significant impact on people’s lives or rights, such as health, education, justice, or public administration. These systems would be subject to strict requirements and obligations before being used in the EU market. Limited-risk AI systems pose some risks to users’ rights or interests, such as chatbots or voice assistants. These systems would only need to comply with transparency obligations, such as informing users that they are interacting with an AI system.
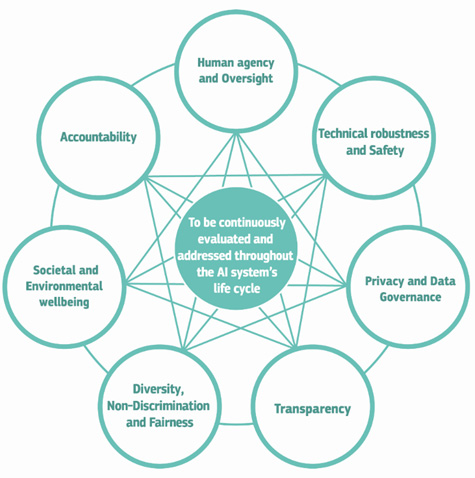
In this article, we will focus on how human oversight and transparency can ensure trustworthy AI for high-risk AI systems, as these are the most relevant and challenging issues for ensuring trustworthy AI. We will also provide some examples of high-risk AI systems and how they could be regulated under the AI Act.
What is human oversight?
Human oversight refers to the involvement of human actors in developing, deploying, and using AI systems to ensure that they respect human dignity, autonomy, and values. Human oversight can take different forms and degrees, depending on the context and purpose of the AI system. For example, human oversight can mean human-in-the-loop (HITL), where a human can intervene and modify the outcome of an AI system; human-on-the-loop (HOTL), where a human can monitor and stop an AI system; or human-in-command (HIC), where a human has the ultimate authority and responsibility over an AI system.
The AI Act requires that high-risk AI systems have appropriate human oversight throughout their life cycle, from design to operation. The level of human oversight should be proportional to the potential impact and severity of harm the AI system can cause. For instance, an AI system that supports medical diagnosis should have a higher level of human oversight than an AI system that supports traffic management. The AI Act also specifies that human oversight should be adequate, meaning that humans should have sufficient knowledge, skills, and authority to oversee the AI system.
What is machine learning transparency?
Machine learning transparency refers to the ability to understand and explain how an AI system works, how it makes decisions, and its limitations and uncertainties. Machine learning transparency can have different levels and dimensions, depending on the audience and purpose of the explanation. For example, machine learning transparency can mean technical transparency, where the internal mechanisms and parameters of an AI system are disclosed; functional transparency, where the inputs, outputs, and performance of an AI system are disclosed; or causal transparency, where the reasons and factors behind the decisions of an AI system are disclosed.
The AI Act requires that high-risk AI systems have adequate machine learning transparency throughout their life cycle, from design to operation. The level of machine learning transparency should be proportional to the potential impact and severity of harm the AI system can cause. For instance, an AI system that affects legal rights or obligations should have more machine learning transparency than an AI system that affects personal preferences or interests. The AI Act also specifies that machine learning transparency should be accessible, meaning that the information provided by the AI system should be understandable and relevant to the users and verifiable, meaning that the information provided by the AI system should be accurate and reliable.
How do human oversight and machine learning transparency interact?
Human oversight and machine learning transparency are closely related concepts that interact differently to ensure trustworthy AI for high-risk AI systems. Human oversight enables machine learning transparency: Human oversight can facilitate machine learning transparency by ensuring that humans can access relevant information about how an AI system works and makes decisions. For example, human oversight can ensure that an AI system provides precise and comprehensible information about its intended purpose, expected performance, limitations, uncertainties, and risks. Human oversight can also ensure that an AI system provides reasons and factors behind its decisions, primarily when they affect people’s rights or interests. Machine learning transparency enables human oversight: Machine learning transparency can facilitate human oversight by providing humans with the necessary information and tools to oversee and control an AI system. For example, machine learning transparency can allow humans to intervene and modify the outcome of an AI system or to monitor and stop an AI system. Machine learning transparency can also allow humans to contest and appeal the decisions made by an AI system or to report and correct any errors or harm caused by an AI system. Human oversight and machine learning transparency complement each other: Human oversight and machine learning transparency can complement each other by providing different perspectives and levels of understanding of an AI system. For example, human oversight can provide a holistic and contextual view of an AI system, while machine learning transparency can provide a detailed and technical view of an AI system. Human oversight can also provide a normative and ethical view of an AI system, while machine learning transparency can provide a factual and empirical view of an AI system.
Conclusion
The EU Artificial Intelligence Act is a landmark regulation that aims to create a legal framework for trustworthy AI in the EU. The AI Act introduces a risk-based approach to regulating AI systems based on their potential impact on human rights and society. Among the critical aspects of the AI Act are the requirements for human oversight and machine learning transparency for high-risk AI systems. These requirements aim to ensure that high-risk AI systems are developed and used in a way that respects human dignity, autonomy, and values.
Human oversight and machine learning transparency are closely related concepts that interact differently to ensure trustworthy AI for high-risk AI systems. Human oversight enables machine learning transparency by ensuring that humans have access to relevant information about how an AI system works and makes decisions. Machine learning transparency enables human oversight by providing humans with the necessary information and tools to oversee and control an AI system. Human oversight and machine learning transparency complement each other by providing different perspectives and levels of understanding of an AI system.
CertX can help you comply with the requirements and obligations of the AI Act by providing you with independent and reliable certification services for your high-risk AI systems. CertX has extensive experience and expertise in functional safety, artificial intelligence, and cyber security, and can offer you tailored solutions to meet your specific needs and challenges. By choosing CertX, you can ensure that your high-risk AI systems are trustworthy, safe, and ethical.